Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*; Machida, Masahiko
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.243 - 256, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.257 - 273, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.01(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)A preconditioned Chebyshev basis communication-avoiding conjugate gradient method (P-CBCG) is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in a multiphase thermal-hydraulic CFD code JUPITER, and its computational performance and convergence properties are compared against a preconditioned conjugate gradient (P-CG) method and a preconditioned communication-avoiding conjugate gradient (P-CACG) method on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 KNLs. The P-CBCG method reduces the number of collective communications with keeping the robustness of convergence properties. Compared with the P-CACG method, an order of magnitude larger communication-avoiding steps are enabled by the improved robustness. It is shown that the P-CBCG method is 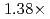 and
and 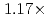 faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.128 - 145, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:10 Percentile:85.61(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)We developed a CFD code based on the adaptive mesh-refined Lattice Boltzmann Method (AMR-LBM). The code is developed on the GPU-rich supercomputer TSUBAME3.0 at the Tokyo Tech, and the GPU kernel functions are tuned to achieve high performance on the Pascal GPU architecture. The performances of weak scaling from 1 nodes to 36 nodes are examined. The GPUs (NVIDIA TESLA P100) achieved more than 10 times higher node performance than that of CPUs (Broadwell).